Ansys LS-DYNA Multiphysics Solver
Hotline: +84 906 988 447
Head Office: Ho Chi Minh City
- Tel: +84 2839 778 269 / 3601 6797
- Email: sales@lidinco.com
- Add: 487 Cong Hoa Street, Tan Binh Ward, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Office: Bac Ninh City
- Tel: +84 222 730 0180
- Email: bn@lidinco.com
- Add: 184 Binh Than Street, Vo Cuong Ward, Bac Ninh, Vietnam
-
 Technical Counseling
100% Free
Technical Counseling
100% Free
-
 Free Shipping
For 3.000.000vnd Order
Free Shipping
For 3.000.000vnd Order
- Impact Analysis
- Forming Solutions
- Euler, Lagrange, and ALE Formulations
- Non-linear Implicit Structural Analysis
- Crash Simulation and Analysis
- Electromagnetics
- Smoothed-Particle Hydrodynamics
- Non-linear Explicit Structural Analysis
- Failure Analysis
- Fluid-structure interaction
- Incompressible Fluid Dynamics
- Total Human Model for Safety (THUMS™)
Ansys LS-DYNA is the industry-leading explicit simulation software used for applications like drop tests, impact and penetration, smashes and crashes, occupant safety, and more.
Simulate the Response of Materials to Short Periods of Severe Loading
Ansys LS-DYNA is the most used explicit simulation program in the world and is capable of simulating the response of materials to short periods of severe loading. Its many elements, contact formulations, material models and other controls can be used to simulate complex models with control over all the details of the problem. Ansys LS-DYNA applications include:
- Explosion / Penetration
- Bird Strike
- Crashworthiness / Airbag Simulations
- Fracture
- Splashing / Hydroplaning / Sloshing
- Incompressible and Compressible Fluids
- Stamping / Forming / Drawing / Forging
- Biomedical and Medical Devices Simulations
- Drop Test of All Forms
- Impacts
- Product Misuse / Severe Loadings
- Product Failure / Fragmentation
- Large Plasticity in Mechanisms
- Sports Equipment Design
- Manufacturing Processes Like Machining / Cutting / Drawing
- Vehicle Crash and Occupant Safety
Key Features
Các thành phần LS-DYNA, công thức tiếp xúc, mô hình vật liệu và các điều khiển khác có thể được sử dụng để mô phỏng các mô hình phức tạp với khả năng kiểm soát mọi chi tiết của vấn đề.
Implicit and Explicit Solvers Easily switch between Implicit and Explicit solvers for your different runs. | |
Frequency Domain Analysis Frequency domain analysis allows LS-Dyna users to explore capabilities such as frequency response function, steady state dynamics, random vibration, response spectrum analysis, acoustics BEM and FEM, and fatigue SSD and random vibration. You can use these capabilities for applications such as NVH, acoustic analysis, defense industry, fatigue analysis and earthquake engineering. | |
ICFD for Incompressible Fluid ICFD solver is a stand-alone CFD code that includes a steady-state solver, transient solver, turbulence model for RANS/LES, free surface flows and isotropic/anisotropic porous media flow. Coupled to structural, EM solver and thermal solver. | |
Electromagnetics Solver EM solves the Maxwell equations using FEM & BEM in the Eddy current approximation. This is suitable for cases where the propagation of electromagnetic waves in air (or vacuum) can be considered as instantaneous. The main applications are magnetic metal forming or welding, induced heating, and battery abuse simulation. | |
Multiphysics Solver Multiphysics Solver include ICFD for Incompressible Fluids, electromagnetic solver, EM for battery abuse, and CESE for compressible fluids. | |
Particle Methods There are several particle methods using LS-Dyna. AIRBAG_PARTICLE is used for for airbag gas particles which models the gas as a set of rigid particles in random motion. PARTICLE_BLAST for high explosive particles which models high explosive gas and air modeled Particle gas. Discrete element method includes applications such as agriculture and food handling, chemical and civil Engineering, mining, mineral processing. | |
Contact – Linear and Nonlinear In LS-DYNA, a contact is defined by identifying (via parts, part sets, segment sets, and/or node sets) what locations are to be checked for potential penetration of a slave node through a master segment. A search for penetrations, using any of a number of different algorithms, is made every time. In the case of a penalty-based contact, when a penetration is found, a force proportional to the penetration depth is applied to resist, and ultimately eliminate the penetration. Rigid bodies may be included in any penalty-based contact but for that contact force to be realistically distributed, it is recommended that the mesh defining any rigid body be as fine as that of a deformable body. | |
Adaptive Remeshing Several tools are provided for local refinement of the volume mesh in order to better capture mesh sensitive phenomenon’s such as turbulent eddies or boundary layer separation reattachment. During the geometry set up, the user can define surfaces that will be used by the mesher to specify a local mesh size inside the volume. If no internal mesh is used to specify the size, the mesher will use a linear interpolation of the surface sizes that define the volume enclosure. | |
Meshless – SPH Ansys LS-DYNA has two different classes of mesh-free particle solvers: continuum-based smooth particle hydrodynamics (SPH), and discrete particle solvers using the discrete element method (DEM), the particle blast method (PBM) and the corpuscular particle method (CPM). These solvers are used in various applications like hypervelocity impacts; explosions; friction stir welding; water wading; fracture analysis in car windshields, window glass and composite materials; metal friction drilling; metal machining; and high-velocity impact on concrete and metal targets. | |
Meshless – ALE Ansys LS-DYNA có hai lớp bộ giải hạt không lưới khác nhau: thủy động lực học hạt mịn dựa trên liên tục (SPH) và bộ giải hạt rời rạc sử dụng phương pháp phần tử rời rạc (DEM), phương pháp nổ hạt (PBM) và phương pháp hạt dạng hạt (CPM). Các bộ giải này được sử dụng trong nhiều ứng dụng khác nhau như va chạm siêu tốc; nổ; hàn khuấy ma sát; lội nước; phân tích vết nứt trên kính chắn gió ô tô, kính cửa sổ và vật liệu composite; khoan ma sát kim loại; gia công kim loại; và va chạm tốc độ cao vào bê tông và mục tiêu kim loại. | |
Advanced CAE Peridynamics & SPG The smoothed particle Galerkin (SPG) method is a new Lagrangian particle method for simulating the severe plastic deformation and material rupture taken place in ductile material failure. The Peridynamics method is another compelling method for brittle fracture analysis in isotropic materials as well as certain composites such as CFRP. These two numerical methods share a common feature in modeling the 3D material failure using a bond-based failure mechanism. Since the material erosion technique is no more necessary, the simulation of the material failure processes becomes very effective and stable. Isogeometric Analysis (IGA) The isogeometric paradigm employs basis functions from computer-aided design (CAD) for numerical analysis. The actual geometry of the CAD parts is preserved which is in sharp contrast to finite element analysis (FEA) where the geometry is approximated with, potentially higher-order, polynomials. Isogeometric analysis (IGA) has been extensively studied in the past few years in order to (1) reduce the effort of moving between design and analysis representations and (2) obtain higher-order accuracy through the higher-order interelement continuity of the spline basis functions used in CAD. LS-DYNA is the first commercial code to support IGA through the implementation of generalized elements and then keywords supporting non-uniform rational B-splines (NURBS). Many of the standard FEA capabilities, such as contact, spot-weld models, anisotropic constitutive laws, or frequency domain analysis, are readily available in LS-DYNA with new features added steadily. | |
Support LS-OPT Ansys LS-OPT is a standalone design optimization and probabilistic analysis package with an interface to Ansys LS-DYNA. It is difficult to achieve an optimal design because design objectives are often in conflict. LS-OPT uses a systematic approach involving an inverse process for design optimization: First you specify the criteria and then you compute the best design according to a mathematical framework. Probabilistic analysis is necessary when a design is subjected to structural and environmental input variations that cause a variation in response that may lead to undesirable behavior or failure. A probabilistic analysis, using multiple simulations, assesses the effect of the input variation on the response variation and determines the probability of failure. Together, design optimization and probabilistic analysis help you to reach an optimal product design quickly and easily, saving time and money in the process. Typical applications of LS-OPT include: Design optimization LS-TaSC LS-TaSC™ is a Topology and Shape Computation tool. Developed for engineering analysts who need to optimize structures, LS-TaSC works with both the implicit and explicit solvers of LS-DYNA. LS-TaSC handles topology optimization of large nonlinear problems, involving dynamic loads and contact conditions. | |
Supporting Tools Dummies Anthropomorphic Test Devices (ATDs), as known as "crash test dummies", are life-size mannequins equipped with sensors that measure forces, moments, displacements, and accelerations. These measurements can then be interpreted to predict the extent of injuries that a human would experience during an impact. Ideally, ATDs should behave like real human beings while being durable enough to produce consistent results across multiple impacts. There are a wide variety of ATDs available to represent different human sizes and shapes. Barriers LSTC offers several Offset Deformable Barrier (ODB) and Movable Deformable Barrier (MDB) models. LSTC ODB and MDB models are developed to correlate to several tests provided by our customers. These tests are proprietary data and are not currently available to the public. Tires LST jointly developed tire models with FCA. These models can be downloaded through the LST, Models download section. The models are based on a series of material, verification, and component level tests. The finite element mesh is based on 2D CAD data of the tire section. All major components of the tire use 8-noded hexahedron elements. The elastomers are modeled using *MAT_SIMPLIFIED_RUBBER and the plies are modeled using *MAT_ORTHOTROPIC_ELASTIC. |
What's New
The 2024 R2 release of Ansys LS-DYNA enables customers to increase efficiency throughout the full workflow for complex multiphysics simulations
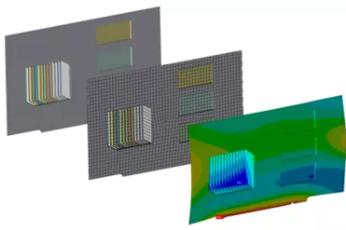 |  |  |
| Simplified Input File Splitting | Streamlined Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH) Simulations | Enhanced Multiphysics Simulations |
| All sections of an LS-DYNA input file can now be easily split and saved into separate sub-input files for use inside and outside of Mechanical. Simplifying the process of modifying or extracting specific sections, such as a mesh, deformed geometry, or named selections, for reuse in subsequent simulations. | Major enhancements to streamline NVH workflows with complex geometries using Boundary Element Method (BEM) acoustic analyses. These include a dedicated BEM acoustics meshing workflow to significantly reduce total meshing time and the integration of the BEM acoustics solver, which can evaluate high frequencies and large frequency ranges without the need to mesh the fluid volume. | Enhancements to multiphysics coupling enable increased accuracy when simulating the impact of structural and thermal induced deformations on electromagnetic components. Applications include battery modeling, electromagnetic forming, induction hardening, and more. |
Accessories
Please login to write review!






